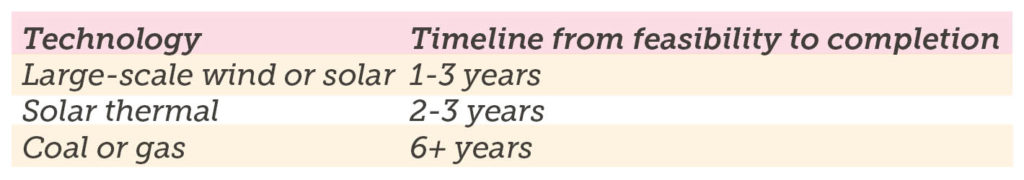Now, before you close the page because, let’s be honest, energy chat isn’t all that entertaining – we promise that at least one of these facts will be the perfect conversation starter at your next summer BBQ.
In the words of Robbie Williams – “Let [energy] entertain you!”
#1
There are literally a handful of people in a bunker in an undisclosed western Sydney suburb controlling the entire National Electricity Market. This is the electricity grid powering the east coast of Australia and South Australia from Port Douglas in the north to Tasmania in the south. 24 hours a day, seven days a week these people are making sure Australians have enough power.
To learn more about the regulators and bodies which govern Australia’s electricity grid, see Who makes the decisions.

#2
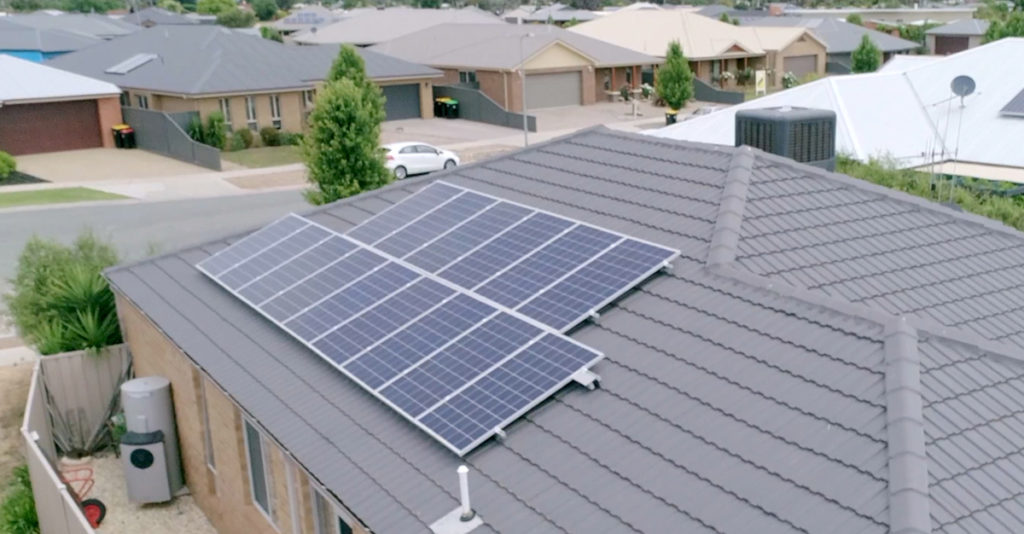
In 2017 more solar was installed globally than coal, gas and nuclear combined.
In 2017, 17 countries generated more than 90% of their electricity with renewable energy. Despite having world-class solar and wind resources, Australia was not one of them. Only 15% of Australia’s power comes from renewable energy sources like solar, wind and hydro.

#3
Energy storage must be paired with renewable energy for it to be ‘pollution-free’.
When storing power from renewables like wind and solar – energy storage technologies, like batteries and pumped hydro, are helping to reduce our greenhouse pollution. However, when energy storage technologies are coupled with fossil fuels this can result in even greater greenhouse gas pollution.
For more, check out Fully charged: Renewables and Storage Powering Australia

#4
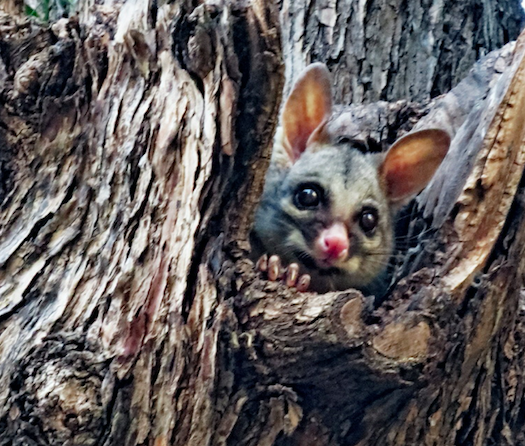
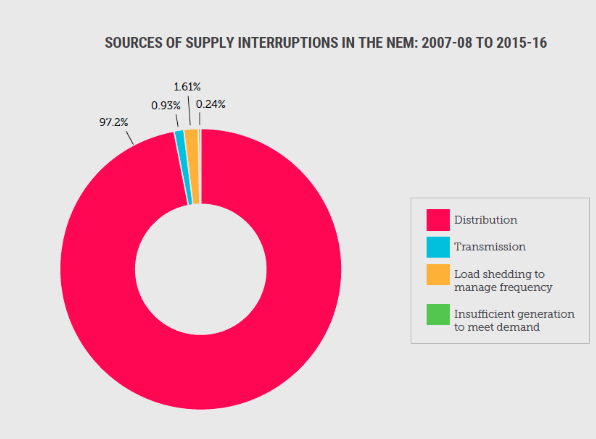
Most blackouts have nothing to do with the supply of electricity (be it coal, gas, wind or solar). In fact, more than 98% of power interruptions are caused by events affecting power lines. The most common causes of blackouts are usually storms, fallen trees, vehicle impacts, bushfires, lightning strikes, heatwaves, birds and possums (like this outage which left 1,300 Brunswick residents without power).
For more information on reliability, see our report: Clean & Reliable Power: Roadmap to a Renewable Future.

#5
Since December 2017, there have been more than 100 breakdowns at fossil fuel power stations in Australia. The situation is made worse in heatwave conditions. On multiple occasions in February 2017 across Queensland, New South Wales and South Australia aging coal and gas power plants operated below capacity or were withdrawn entirely due to technical faults caused by the heat. This is not ideal in a ‘sunburnt country’.

#6
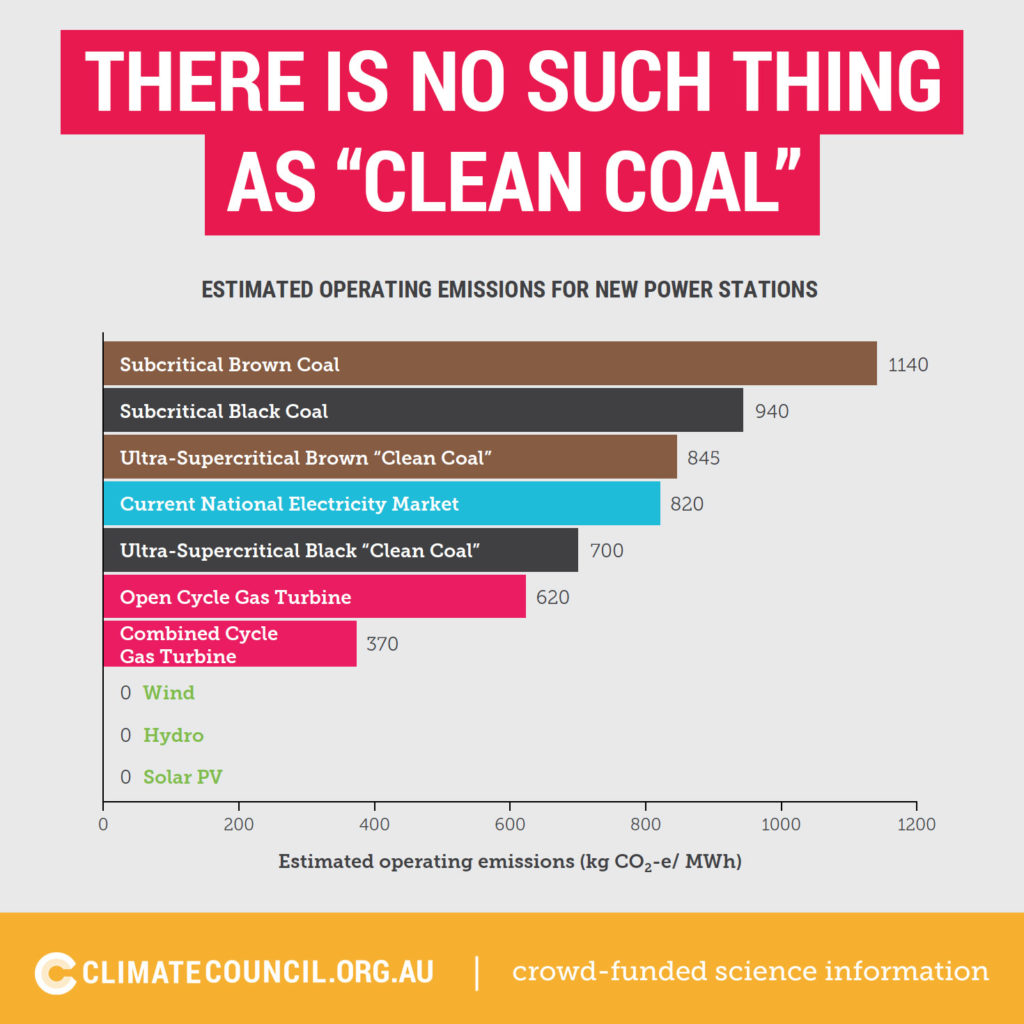
There is no such thing as clean coal. On greenhouse gas pollution, brown coal is worse than black coal.
And, did you know, coal power stations with carbon capture and storage (CCS) can actually end up polluting more? There are only two operational coal power stations with CCS in the world. Both of these power stations capture only a small part of their greenhouse gas pollution and pump it underground as a means to extract oil. Once this extracted oil is burnt, the coal power stations with CCS end up causing more greenhouse gas pollution than a standard coal power station. The CCS process for the Petra Nova power station in the United States results in 32% more carbon dioxide emissions overall due to the additional oil extracted.
For more, read End of the Line: Coal in Australia
#7
Australia is now the world’s largest gas exporter.
Producing and exporting liquefied natural gas (LNG) is driving dramatic growth in Australia’s greenhouse gas pollution. The growth of LNG exports has also led to rising and increasingly volatile gas prices here in Australia.
#8
Renewable energy is the quickest and cheapest form of new energy generation. Renewables have much lower capital costs and are quicker to build when compared to coal.
Costs for new energy generation:
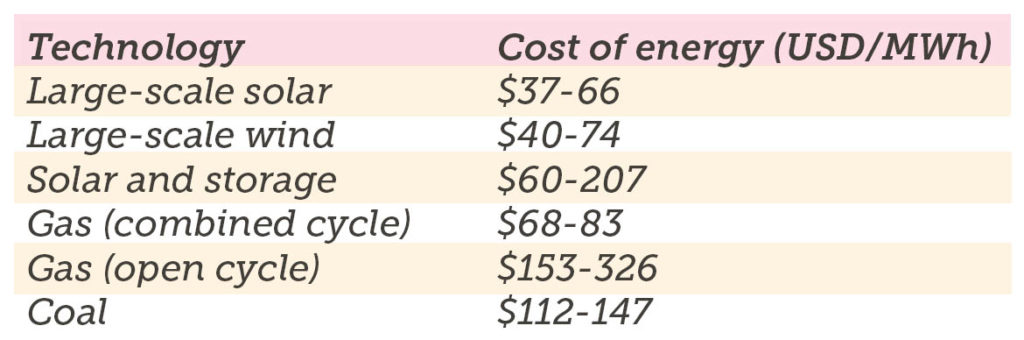
Timeframes for power projects:
For more information, check out Electricity Prices: Sorting Fact From Fiction.
#9
What about nuclear? Nuclear power isn’t technically “renewable”.
While there is no emissions associated with the nuclear reaction itself, nuclear is far from low emission energy. Greenhouse gas pollution associated with nuclear power could be similar to a gas power station, due to mining, construction, decommissioning and waste management.
Nuclear power plants are highly controversial and cannot be built under existing laws in any Australian state or territory.
Nuclear power plants are far more expensive than renewable energy and take almost a decade to build (a nuclear power station under construction now in the UK is set to cost 20 billion pounds – AU$36 billion). Building a nuclear power station in Australia would likely take even longer given the need for legislation change, public attitudes towards nuclear and the lack of relevant local skills or industry knowledge. And anyway, there’s no need for nuclear power in a country blessed with so much sun and wind.
Also, in Australia, it is pronounced “nuclear” not “nucular”

For more information check out – Nuclear power stations are not appropriate for Australia – and probably never will be.
#10
Finally, our personal favourite – if you tell your power company that you want 100% renewable energy they have to do it. By making this choice, Australians can help install more renewable energy than what’s specified under the Renewable Energy Target.
For more, read What is GreenPower?
So, there you have it – our fav energy tidbits!

10 facts not enough for you? Head to our website Energy Facts Australia.